This presentation offers an in-depth overview of modern security system solutions, detailing core technologies, their integration, benefits, and strategic implementation for organizational safety.
Key Security System Components
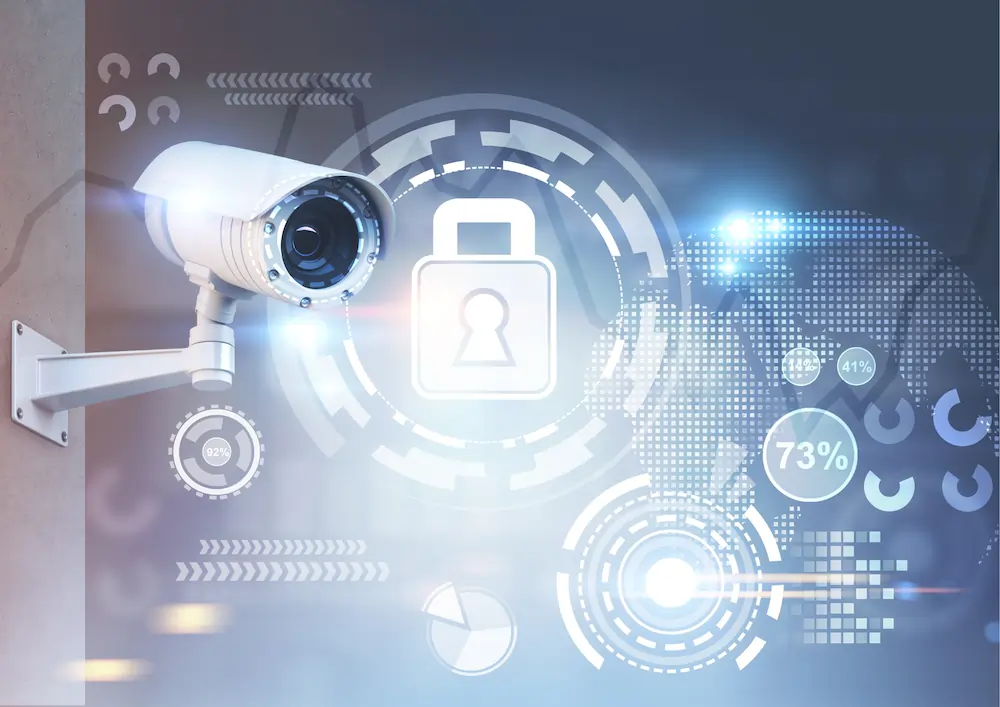
1. CCTV Systems
- Purpose: Constant monitoring, deterrence of crime, and evidence collection.
- Modern Features: High-definition video, night vision, remote viewing, and smart analytics to identify suspicious behaviors automatically.
Explained: CCTV (Closed-Circuit Television) Systems use cameras to surveil areas and record footage. Video analytics refers to software that can identify abnormal activities (e.g., trespassing) and alert security staff automatically.
2. Access Control Systems
- Function: Manage and restrict entry to sensitive areas, preventing unauthorized access.
- Types: Range from key cards to sophisticated biometrics (fingerprint or facial scans).
- Benefits: Real-time oversight, easy modification of access rights, and record-keeping for accountability.
Explained: Access control refers to systems that determine who can enter certain areas. Audit trails are records showing who accessed what area and when.
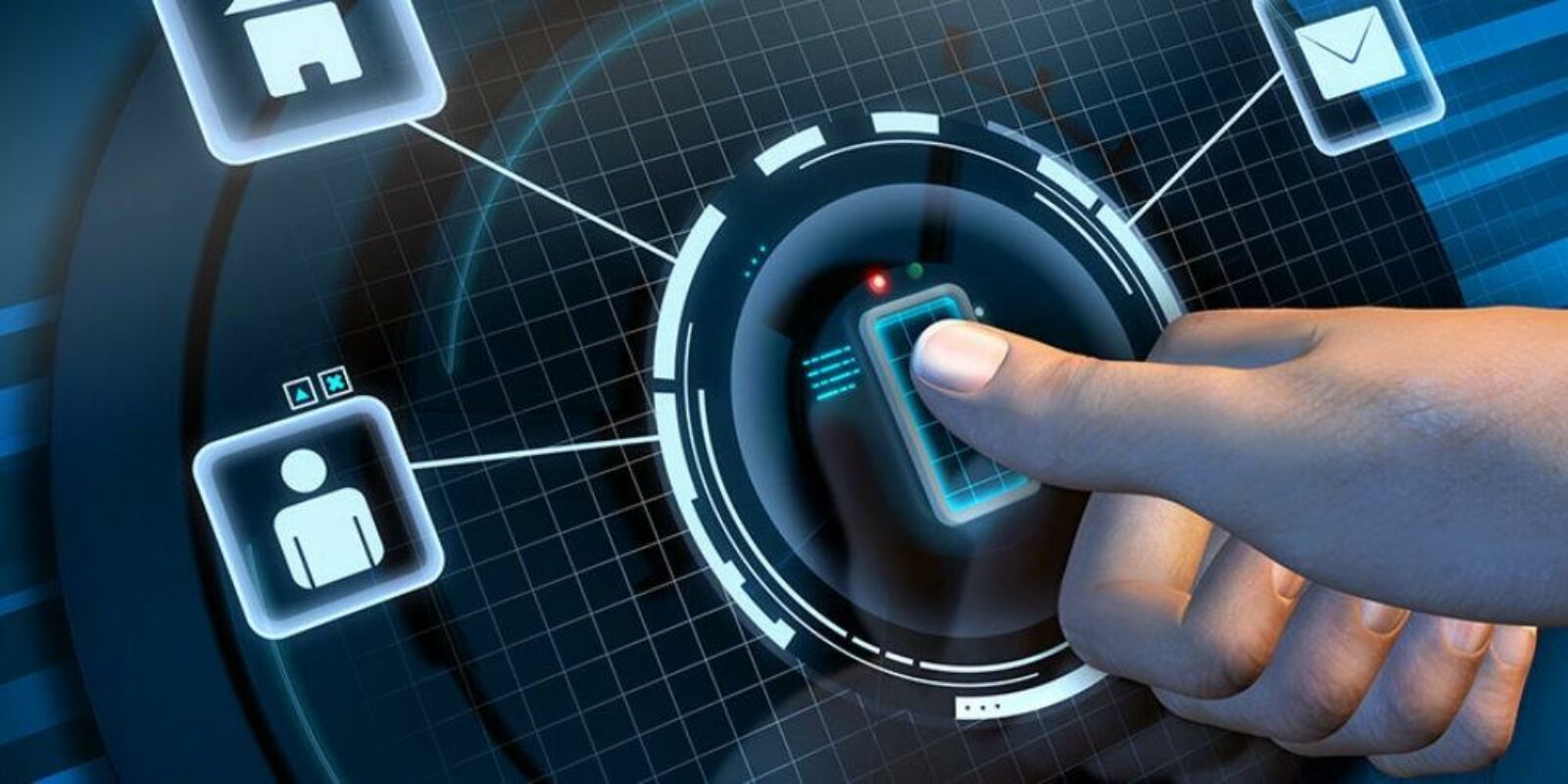
3. Biometric Systems
- Authentication: Uses unique biological traits (e.g., fingerprints, iris, face) for secure access.
- Advantages: High fraud resistance and user convenience, reducing risks of stolen passwords/cards.
Explained: Biometrics involves personal biological data used to verify identity, making impersonation extremely difficult.
4. Intruder Alarm Systems
- Purpose: Detect and respond to unauthorized entry through motion sensors and alert mechanisms.
- Benefits: Immediate notifications for rapid response, strong deterrence for potential intruders.
5. Fire Alarm Systems
- Role: Early detection and alerting in case of fire (using smoke, heat detectors, and manual alerts).
- Importance: Enhances safety and aids compliance with safety regulations.
Integrated Security Solutions
- Synergy: Combining multiple systems (CCTV, access control, alarms) into a unified management platform.
- Advantages: Centralized control, improved situational awareness, and streamlined incident response.
Explained: Integration means these systems work together seamlessly, usually through a central interface, for more efficient management.
Choosing the Right Security Partner
- Criteria: Consider expertise, track record, certifications, and support capabilities.
- Value: Seek partners offering scalable, customizable, and well-supported solutions for long-term protection.
Case Studies & Success Stories
- Showcases of industry-specific deployments illustrating how tailored security implementations overcome unique challenges and enhance safety outcomes.
Next Steps & Engagement
- Participants are encouraged to ask questions, engage in consultations, and consider customized solutions based on their unique requirements.
Conclusion
- Effective security requires integrating multiple advanced technologies—CCTV, access controls, biometrics, alarms—delivered by knowledgeable partners.
- The overarching goal is to provide robust, intelligent, and adaptable protection frameworks for people, assets, and environments.
Glossary of Key Terms
| Term | Explanation |
| CCTV | Closed-Circuit Television, for video surveillance. |
| Access Control | Systems managing and restricting entry to areas. |
| Biometric | Technology using unique biological characteristics for identification. |
| Analytics | Software that interprets surveillance data to detect anomalies. |
| Audit Trail | Records of access and activities for accountability. |
| Integration | Combining multiple security systems for unified management. |
For further clarification or personalized recommendations, participants are encouraged to request consultations.